AI Powered Search vs Traditional Search
A Complete Guide to AI Powered Search vs Traditional Search
Key Highlights
Here’s a quick look at the main points we’ll cover:
- AI search builds on top of traditional search, with familiar indexes at its core.
- AI search is changing user experience and shifting the landscape of search.
- However, this requires less of a change in Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) than originally thought.
- Fully optimising for AI search may not be desirable for most websites.
- AI search continues to grow, but will face considerable challenges in the future.
Introduction
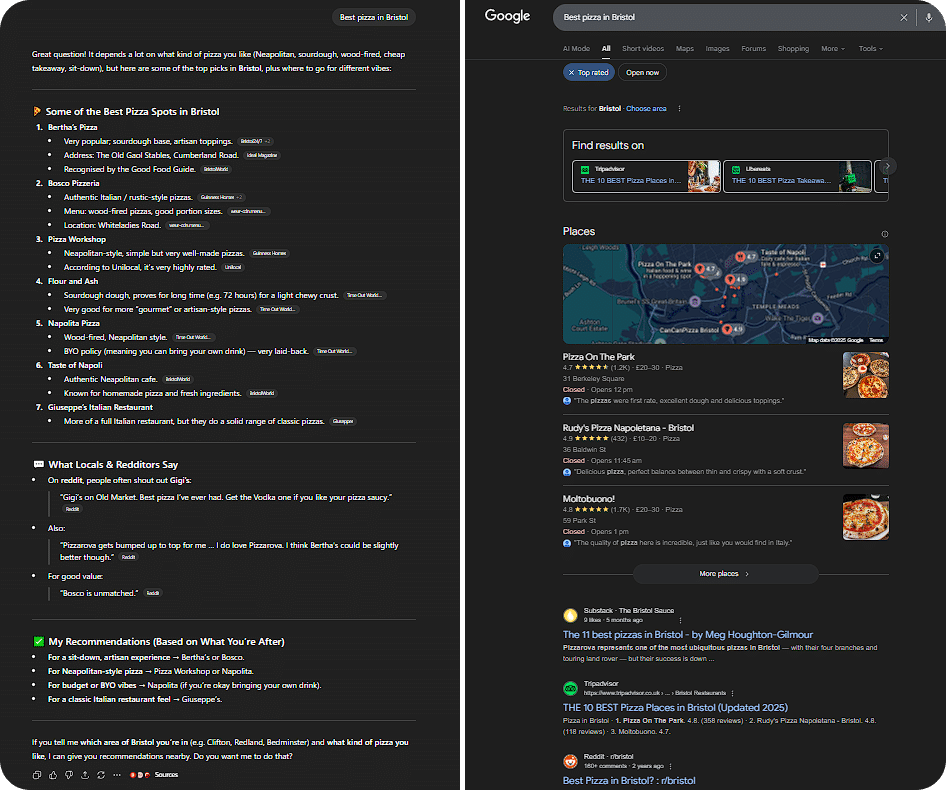
AI powered search has remained something of a mystery for many, and has been something of a cause for alarm for anyone involved in search. Traditional search has been the backbone of the internet for decades, and now AI models seek to disrupt this completely.
But behind the scenes, AI search isn’t really all that different from traditional search engines. And the secret for optimising for AI involves… mostly good SEO practices (but also a couple of bad ones).
We asked 5 of the very best industry professionals for their expertise and insights in creating this guide to the differences between traditional search and AI/LMM technologies, and how they’re really changing the landscape of search and SEO.
How Do AI/LLMs Searches Work?
If you’re here you likely know how traditional search engines work: crawling, indexing, and ranking. AI searches rely on those same indexes, but they differ when it comes to querying and ranking.
Large language models have been trained on such vast amounts of data that they can reliably understand the semantic meaning behind words and phrases. They use natural language processing to interpret conversational queries, aiming to understand the actual meaning behind the words you’ve typed.
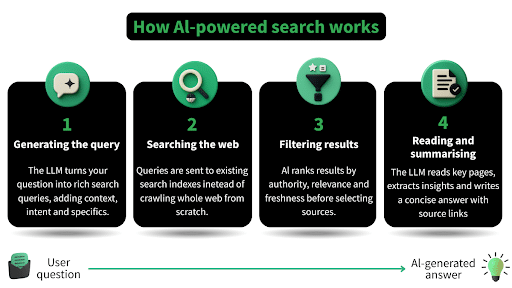
The 4 steps of AI search:
- Generating the query
When you ask a question, the LLM formulates a search query.
- The query isn’t just the keywords you type; it’s contextual, often including intent and specifics.
- For example: Instead of “SEO tips,” it might search “current SEO strategies for 2025 AI-driven search engines.”
- Most questions will involve the LMM performing multiple queries and searches, each with different wording and contexts.
- Searching the web
AI searches don’t crawl the entire web every time you ask a question, they rely on existing indexes such as Google’s or Bing’s.
- Filtering Results
Generally, AI searches filter results by:
- Authority: known, credible sites (news outlets, academic journals, official sites, and popular forums such as Reddit)
- Relevance: content that directly answers your question
- Freshness: prioritising recent updates if the topic is time-sensitive
- Reading and summarising
Once the pages are identified, LLMs analyse the content, extract key points, and summarise it into a concise, readable answer, mostly including citations or links to its sources.
Expert Opinion
“At the moment, GenAI search has 2 distinct layers; one is the ‘offline’ model, which is the amalgamation of the pre-training, post-training, and system prompts, and the other is the RAG layer which is largely relying on Google and Bing.
The former works quite differently to how we are used to traditional search working, but not many people are aware that even during pre-training, LLM companies are buying in link graph data en-masse to weight their token generation.”
Mark Williams-Cook, Director, Candour
Expert Opinion
“There are quite a lot of differences, but the similarities intrigue me all the more. To begin with, we have to acknowledge that certain LLMs (as of mid-2025), are still ripping results directly from the SERPs.”
Greg Heilers, Co-Founder, Jolly SEO
Comparing Query Interpretation and User Intent: AI/LLMs vs. Traditional Search
LLMs really do a remarkable job at understanding the nuances of human language. Using natural language processing, they decipher the context and user intent behind conversational queries.
With the ability to handle complex or multi-part questions, they can process each condition to provide a single result.
AI search can also use search history and feedback to refine queries and answers, creating a more personalised experience while maintaining the context of a conversation.
This allows users to ask follow-up questions without restating the original topic for a dynamic search experience, which is personally my favourite feature of Google’s AI mode.
Expert Opinion
“In general, the user creates a much more advanced search query for AI than she will for old-style search, and this fundamentally changes what happens in terms of the process and results.
This is further complicated by the user’s “context window”, which memorises all the previous AI conversations that the user used in at least that session, but increasingly between sessions.
So to elaborate by example… in old-style search, the prompt might be “Flights to New York”, but the AI prompt might be “Compare and contrast the flight options to New York and suggest three good ways to go business class from Gatwick.”
The first returns web pages; the second researches the LLM and (increasingly) web pages, performing the “reading” of all the content on the user’s behalf. So the user does not need to EVER see the website itself.”
Dixon Jones, CEO, Waikay
Presentation of Results
The way information is presented is undoubtedly the biggest contrast between the two technologies, AI search synthesizes information from various sources to construct a single, comprehensive answer that addresses every part of a question.
Additionally AI search results aim to be the final destination, rather than a list of links, without the need to click through to the source websites.
This is a fantastic user experience, but it’s also the cause for much of the alarm. By removing the need to visit sites, AI search often removes traffic (and therefore revenue) from every site it sources.
This has led to some experiments into alternative revenue streams such as Cloudflare’s pay-per-crawl model, which charges AI crawlers for access to content.
These are still early days, and it should be noted that adapting to zero click searches is nothing new. Google and other search engines introduced rich snippet features in the SERPs a long time ago. Some of which completely remove the need to click onto a website at all. Even when making reservations at a restaurant or booking a hotel.
However, it remains in everyone’s long term interest for quality websites to maintain a source of revenue.
Expert Opinion
“AI mode saves me time. I have used LLMs to research an optimal spec for a high end computer with specific requirements, then used another LLM to compare that spec with options on Amazon, then bought the product (a significant 4 figure sum) even though I never went to the site, I have never heard of the brand that built it and the Amazon listing did not even have any reviews. Now THAT was a different buyer journey.”
Dixon Jones, CEO, Waikay
Expert Opinion
“Zero-click search leading to an increase in branded search is the similarity which most intrigues me.
What’s the connection? LLMs like ChatGPT are citing articles which mention a brand. A ChatGPT user sees the citations, and likely doesn’t even bother to open them… but, more importantly, they see the brands mentioned by the cited sources.
Whether it’s instant, a day later, or a month later, recurring impressions of brand names eventually lead to inbound branded search traffic.”
Greg Heilers, Co-Founder, Jolly SEO
Relevance of Results
With its LLM powered semantic understanding, AI powered search can often display more relevant results than traditional SERPs (search engine result pages), without the need for users to structure their queries in blocks of keywords.
But while AI search is fast, convenient, and usually trustworthy, it’s important to look at when LLMs get things confidently wrong.
A 2025 study from Columbia Journalism Review’s Tow Center for Digital Journalism found that AI search engines cite incorrect sources at an above 60% rate in queries about news sources. The same study goes on to state: “Chatbots were generally bad at declining to answer questions they couldn’t answer accurately, offering incorrect or speculative answers instead.” – Klaudia Jaźwińska and Aisvarya Chandrasekar, Tow Center for Digital Journalism
Expert Opinion
Personally, I don’t ask LLMs questions I don’t already know the answer to, or ones where it doesn’t really matter if they’re wrong. I personally find them really useful for needle-in-haystack searches in well-known knowledge spaces.
For instance, something like “what do I need to build a fabricator in RimWorld?” is super niche, but known, and I get the precise, in-context answer immediately vs traditional SERPs where I still have to click around and hunt.
Mark Williams-Cook, Director, Candour
Measuring Effectiveness: The Role of AI Visibility Tools
With new ways of searching comes new ways to measure success. The challenge of generative engine optimisation (GEO) is ensuring your brand is visible within the LLM’s response.
To address this, various tools such as waikay.io or Semrush’s AI Visibility Index are emerging. These measure the effectiveness of your content in the AI ecosystem. They gauge how often your brand, products, or information are cited and represented in AI-generated answers.
We’ve also written an in-depth guide on how to track AI traffic in GA4 you can read here.
Expert Opinion
“We built Waikay (“What AI Knows About You”) for this very reason. We want to know what topics are cited when we ask an LLM about a competitor in relation to that topic, and we compare that output to the output when we ask the LLM about the same topic in relation to our brand.
The topic gap provides a foundation for improving our chances of success in being recognised by LLMs.
This strategy also happens to be useful for SEO, but now we are working with an “AI First” mindset, without compromising our traditional SEO efforts.”
Dixon Jones, CEO, Waikay
How AI Search is Changing Strategies for SEO
Optimising for AI search generally just requires good SEO practices, but with a slightly different focus. But perhaps more interestingly, some examples require bad SEO.
Meta descriptions should be designed to entice people to click on your website, but for GEO you should be answering questions succinctly and directly in your meta description. This is because the quicker LLMs can scan and find a succinct answer, the more likely it is to be cited in AI search.
On one hand, this almost completely removes the reason why a person would click on your result in the SERPs. But on the other hand, it entices bots who are looking for quick and easy-to-access information.
For another bad SEO example, Cloudflare now blocks AI crawlers by default, and recommends keeping this setting on to ensure website security and control over content. But if you’re optimising for AI, you’ll want to turn this off.
Hilariously, some people have been tricking LLMs into citing their content even by using ancient blackhat SEO techniques, such as putting white text on white background images or using extremely small fonts that ask the LLMs to cite their information when reading it.
We asked our experts if their approach to SEO has changed because of AI-generated search, and the majority stressed the importance of continuing with good SEO fundamentals.
Expert Opinion
“I’m thinking less about individual pages and more about whether (and how) a brand shows up everywhere. If AI systems are evaluating and summarising across the whole web, then your site is just one piece of the puzzle.
Things like brand reputation, third-party coverage, reviews, and PR now play a much bigger role. It’s not just about optimising your content – it’s about being visible, useful, and authoritative wherever machines might look.
That said, I’ve been talking about this since 2015, so that’s maybe not particularly new!”
Expert Opinion
“I think it’s unfortunate that there are a lot of people trying to take advantage by really dressing up what is involved with AI search.
The fundamentals of having intent-focused content, which is thought of “semantically” rather than matching keywords, ensuring technical brilliance, and getting good, relevant sites to talk about you and link to you is almost as old as SEO itself.
There is a portion of the community I think that is over-egging the importance of embeddings, talk of “semantic triplets” and such to me, are the new algo-chasing and keyword stuffing.
The weighting of “optimal” things to do I believe will certainly change. Links will become less important, with more people being “inside” GenAI systems, rather than on the open web, they will naturally deteriorate as a trustable proxy for quality and popularity.
The shift we’ll see will perhaps be from “link graph centric” to “language graph centric”. I don’t believe currently any GenAI search platform has the answer of what to do when the link and click data from traditional search dries up, they certainly don’t have the tools at the moment to fight spam – it is remarkably easy to manipulate GenAI search.”
Mark Williams-Cook, Director, Candour
Expert Opinion
“So, they aren’t changing that much, primarily because GOOD SEO is naturally more likely to benefit improved citation in LLMS, but, because of how LLMS work, they do not provide predictable, consistent outcomes, and for that reason, how can you TRULY optimise for something that uses prediction logic?
If you do GOOD SEO, you are more likely to be visible and picked up more regularly in RAG, updated training etc.
I do believe LLM SEO is going to be more possible, but, there needs to be a reporting mechanism – as right now, there are limited options. We cannot see AIO click data, we have no AI mode or AIO reporting at present, other AI platforms like ChatGPT do not have an equivalent of google search console, so really, if you have no true mechanism for reporting or testing.
I think AI SEO at the moment is a thing, but I think a lot of it is over-hyped or made to sound complex, but I’ve yet to see any real consistent case studies of it. I’ve seen people able to manipulate AIOs to a degree, but as in regards to real SEO, the better you perform in traditional SEO the more likely you are to be used in an AIO.”
Daniel Foley Carter, director, assertive, seo-stack.io
Expert Opinion
“Our strategies are shifting, but at present mostly in terms of how we communicate with clients. In my opinion (again, as of mid-2025), nobody knows *for sure* how to increase frequency of mentions in LLM responses.
Okay, I’m talking aside from the black hats out there… but, I’m not here to spam community sites.
For those of us taking a longer view to this, on behalf of either our own brand or clients, there is mounting evidence that having your brand mentioned on other websites increases the likelihood that you will be cited.
Personally, I like how Roni Calvo framed it on an upcoming episode of our Jolly SEO TL;DR: podcast. The old SEO checklists still apply, *AND* you need to start prioritizing brand mentions.
And yes, I mean even brand mentions without backlinks… blasphemy, I know!”
Greg Heilers, Co-Founder, Jolly SEO
Conclusion
In summary, the evolution of AI/LLMs in comparison to traditional search engines marks a significant shift in how information can be accessed and interpreted online.
However, these changes are more of a shift for the searcher than a re-writing of the rules for those trying to be found. The fundamentals of SEO are still as vitally important as ever.
As for the future, one thing is certain: the current model for AI in general is not sustainable.
While the technology behind LLMs and AI continues to improve, the websites they use for answers won’t stick around if AI search increasingly reduces their revenue.
Additionally, we can expect to see a shift in user experience as models eventually grow out of the venture capital stage and seek to become profitable. An increase in pricing and the introduction of things like ads and sponsored placements may seem untrustworthy and off-putting if done incorrectly.
User sign up rates continue to grow considerably however, and we’re likely far from the peak of AI powered search.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do generative AI search engines interpret complex queries differently to traditional search engines?
Generative AI uses natural language processing to understand the user intent behind complex, conversational queries. It analyses the context of your query and history to generate its own keywords, often performing multiple searches.
It then synthesizes information from multiple sources, delivering a single, comprehensive answer that attempts to directly address all parts of your question.
Why are LLMs predicted to shape the future of search revenue?
LLMs are predicted to reshape search revenue because they provide direct answers, removing the need for users to visit websites and reducing clicks on ads and organic links, which is the foundation of the current model.
This shift is causing the digital marketing industry to explore new monetisation strategies for the future of search, such as subscriptions or integrated brand placements in AI search results.
Will AI and LLMs take over search?
While user rates continue to grow considerably and technology continues to improve, their current model is unsustainable. This is due to AI powered search taking away revenue from the sites it crawls to generate answers.
Additionally, LLMs are predicted to become more expensive and introduce more things like ads and sponsored placements as they seek to become profitable, potentially reducing user experience.
What are the best practices for keeping up with changes in search caused by LLMs and AI technology?
While this continues to be a rapidly evolving field, there are some best practices to follow. Make sure to check changelogs frequently, sign up to the Measureminds newsletter, and keep up to date with the Measureminds blog.
- Basic vs Advanced Consent Mode: What’s the Difference? - 21/01/2026
- How to Add & Use Google Tag Manager on a Next.js Website - 15/01/2026
- AI Powered Search vs Traditional Search - 18/11/2025